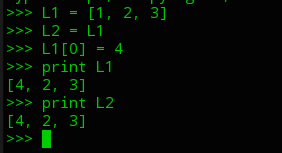
Lec16.
Class:
- template for data type
- cluster data & method
- modularity/abstraction
- data hiding:only acess the parts though a method
- class used to make instances
Encapsulation:(封装)
- data hide
- inheritance:继承
- shadow/override methods
- hierarchy of classes
Lec17.&Lec18.
- Informal problem description to a formal problem statement:把一个非正式的问题转化到一个更加通用的模型上来
- Inventing computational models:创造计算模型
- dealing with & exploiting randomness:探索随机性
- making sense of data:让数据变得有意义,如何理解数据
- evaluating quality of answers:如何来判断和分析程序给出的答案是不是我们所想要的答案
随机走动:
- simolate(模拟) random walk(无规则运动)
- 数据抽象
- Location
- compass Pt
- Field
- Drunk
- pseudo random(伪随机)
课程使用的代码:
import mathimport randomimport pylab
class Location(object):
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = float(x)
self.y = float(y)
def move(self, xc, yc):
return Location(self.x + float(xc), self.y+float(yc))
def getCoords(self):
return self.x, self.y
def getDist(self, other):
ox, oy = other.getCoords()
xDist = self.x - ox
yDist = self.y - oy
return math.sqrt(xDist**2 + yDist ** 2)
class CompassPt(object):
possibles = ('N', 'S', 'E', 'W')
def __init__(self, pt):
if pt in self.possibles:
self.pt = pt
else:
raise ValueError('in CompassPt.__init__')
def move(self, dist):
if self.pt == 'N':
return (0, dist)
elif self.pt == 'S':
return (0, -dist)
elif self.pt == 'E':
return (dist, 0)
elif self.pt == 'W':
return (-dist, 0)
else:
raise ValueError('in compassPt.move')
class Field(object):
def __init__(self, drunk, loc):
self.drunk = drunk
self.loc = loc
def move(self, cp, dist):
oldLoc = self.loc
xc, yc = cp.move(dist)
self.loc = oldLoc.move(xc, yc)
def getLoc(self):
return self.loc
def getDrunk(self):
return self.drunk
class Drunk(object):
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def move(self, field, time=1):
if field.getDrunk() != self:
raise ValueError('Drunk.move called with drunk not in field')
for i in range(time):
pt = CompassPt(random.choice(CompassPt.possibles))
field.move(pt, 1)
def performTrial(time, f):
start = f.getLoc()
distances = [0.0]
for t in range(1, time+1):
f.getDrunk().move(f)
newLoc = f.getLoc()
distance = newLoc.getDist(start)
distances.append(distance)
return distances
# assert False
drunk = Drunk('a man')
for i in range(3):
f = Field(drunk, Location(0, 0))
distances = performTrial(500, f)
pylab.plot(distances)
pylab.title('random walk')
pylab.xlabel('time')
pylab.ylabel('distance from origin')
pylab.show()
assert Falseperform trial 的解释:
- inner loop that simolates 1 trial
- ‘enclose’ inner loop in a loop that conducts appropriate of trials
- calculate and present statics
随机运动的应用:
- Browning motion:布朗运动
- stock market:预测股票
- kinetics
- evolution