Lec7
Python数组:
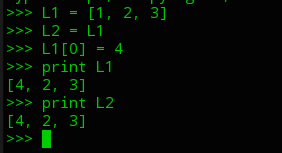
解释: L2 = L1 ==> 创建了一个L2和L1进行绑定,事实是L1和L2绑定了同一个对象,所以在通过L1改变了该对象的时候,L2也会发生变化,其实不是L1,L2的变化而是他们共同绑定的对象的变化.
Dictionaries(字典):
- mutable
- not ordered
- generalized indexing
Pseudo code(伪代码):利用伪代码来控制程序流,拆分模块以及搞清对数据的操作
模块性和封装:不需要关心内部的具体实现,只需要调用就可以
efficiency-orders of growth(算法复杂度,运行效率):
- 为什么我们需要考虑效率:因为问题的复杂度的增长速度远比计算机的发展更快
- choice of algorithm:在遇到问题时,能够选择现有的算法并使得解决问题的效率加快
- map problem into class of algorithm:将问题映射到一类算法
Space & Time:
- how much memory to complete
- what is it of basic steps needed as a function of the input size
Random access model:假定我们在读取任意一块内存区域的时候花费的时间是恒定的(理想状态)
- best case -> Min
- worst case -> Max
- expected case -> Avg
Lec8
例子 整数a的b次幂的计算:
Iterative exponent:
def exp1(a,b):
ans = 1
while (b>0):
ans += a
b -= 1
return ans总共进行了2+3b步
O(b) -> liner
复杂度增长:
- Asymototic notation
- Big O notation - upper limit to growth
Recursive exponent:
def exp2(a,b):
if b == 1:
return a
else:
return a*exp2(a,b-1)分析递归式程序的复杂度:
t(b) = 3 + t(b-1)
= 3 + 3 + t(b-2)
= 3*k + t(b-k)
Done b-k = 1==> O(b)
二分:
a ** b = (a*a) ** (b/2) -> b even
= a*(a**(b-1)) -> b odddef exp3(a,b):
if b == 1:
return a
if (b%2)*2 == b:
return exp3(a*a, b/2)
else:
return a*exp3(a,b-1)==> O(log b)
b even t(b) = 6+t(b/2)
b odd t(b) = 6+t(b-1)
==>t(b) = 12 + t(b/2)
= 12k + t(b/2**k)
k = log2(b)汉诺塔:
- 经典的递归
- O(2**n) -> 指数爆炸
Lec9
二分查找算法:
思想:
- 1.确定first, last, mid=(first+last)/2
- 2.判断如果mid是要找的值==>找到,否==>小于找左边,大于找右边
- 3.mid=first || mid=last goto 1
缺点: 列表(list)不能用二分查找(效率低,复杂度变成线性复杂度)
Generalize:
- pick the mind point
- check to see if this is answer
- if not, reduce to smaller problem.Repeat
Question:
- should we sort before search? ==>
liner search n || sort & search nlogn+logn - can we sort in sub-liner time? - No
- how fast can we sort? — nlogn
Amortize the cost:(平摊花费),如果只搜索一次的话,liner search效率更高,如果搜索多次的话,那么先排序就会体现优势在平摊了排序的花费,而查找的效率是logn.
排序算法
- 选择排序 循环不变量:数组被分成2部分,pre和suff,前部分在排序中是有序的部分,每次只对后部分进行排序到有序为止.
- 冒泡排序